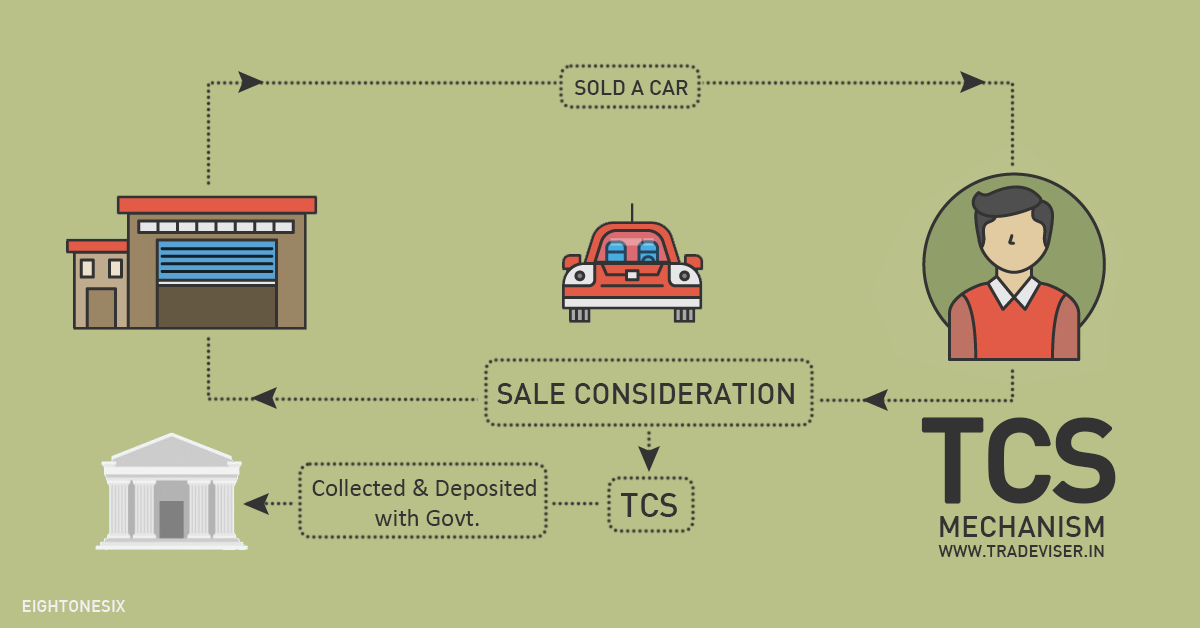
TDS- Tax Deducted at Source
Tax Deducted at Source (TDS) is a tax mechanism introduced by Income Tax Department, where a payer responsible for the payments such as salary, commission, professional fees, interest, rent, etc. is liable to deduct a certain percentage of tax before making payment in full to the receiver of the payment. As the name suggests, TDS is a Tax that is deducted from its source. Tax Deducted at Source is a measure initiated by The Government of India in order to collect indirect Taxes, as per the Income Tax Act, 1961. Tax Deducted at Source that comes under IRS (Indian Revenue Service) is directly managed by CBDT (The Central Board of Direct taxes). The primary motive behind collecting TDS is to keep the revenue source stable for the Government throughout the year. It also prevents people from evading taxes. TDS is mandatory for all those who fall under the Tax Audit Bracket. Failing to comply with Tax Deducted at Source Compliances may attract heavy penalties, interests, and fees. Every business deducting amount at source shall mandatorily hold TAN and shall quote the same in all related documents like TDS-certificate, returns, etc. You must file your TDS returns by 15th of July, October, January, and May; defaulting the same can attract heavy penalties
For example:
A provides technical services to B for 50,000 INR,
B is liable to deduct TDS @ 10%, i.e 5,000 INR and A receives 45,000 INR
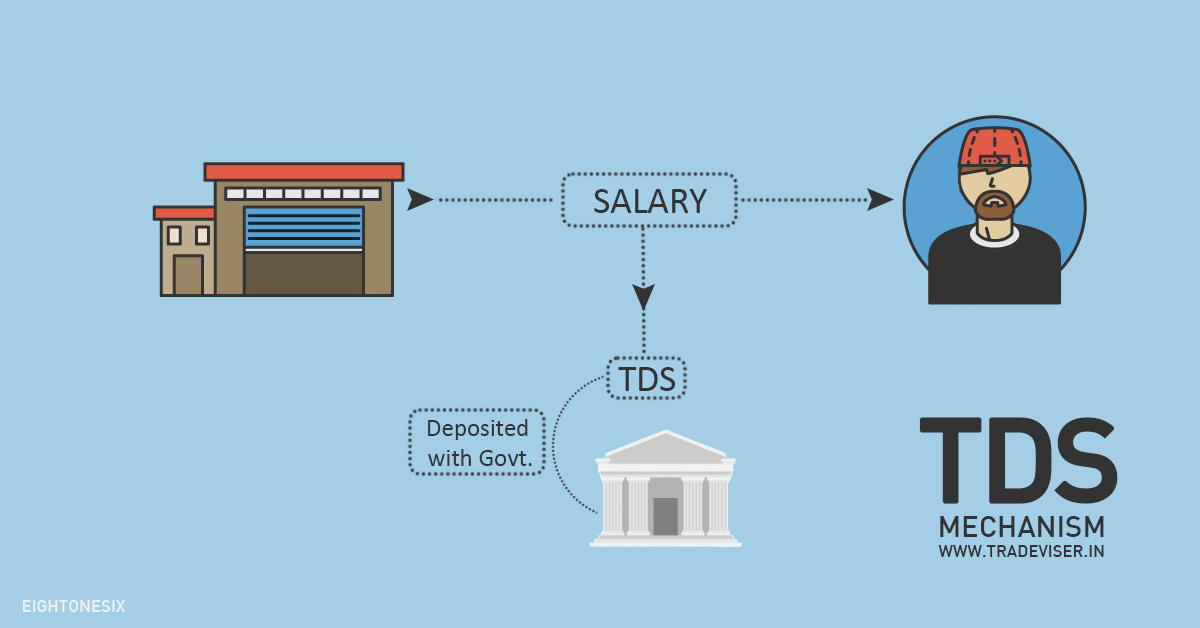
TCS-Tax Collected at Source
TCS or Tax Collected at Source is a mechanism where the receiver extracts a certain amount as the tax of the payer and deposits the same with the government
For example
A is selling a Motor Car worth 12 Lakhs,
A is liable to collect TCS @ 1% on the sale consideration and deposit the same with Govt.
B pays 12.12 Lakhs (12 Lakhs + 1%)