Form 15CA Filing in India: Complete Guide for Overseas Remittances, Steps, and Compliance
Form 15CA is a critical compliance requirement when making cross‑border payments from India. Mandated by the Income‑tax Department, it is used to report remittances and ensure proper Tax Deducted at Source (TDS) or withholding tax compliance. Non‑compliance can lead to penalties and even block your remittance process. As a chartered accountant, I have helped numerous clients navigate Form 15CA effectively. This guide explains its purpose, categories, required documentation, filing steps, and common mistakes to avoid.
What is Form 15CA and Why It Matters
Form 15CA is an online declaration required before transferring funds abroad by any person individual, firm, company, or entity. Its primary objectives are:
-
Ensure the payer has deducted or verified that tax is deducted at source on the payment.
-
Provide a reporting channel for the Income Tax Department to track foreign remittances.
-
Facilitate cross‑border payments while maintaining tax compliance across jurisdictions.
Form 15CB, which is prepared by a Chartered Accountant, is sometimes used in conjunction with Form 15CA to certify the calculation of tax liability. Not all remittances require Form 15CB, but Form 15CA is mandatory in most cases.
Legal Basis: Section 195 and Rule 37BB
The requirement for Form 15CA arises under Section 195 of the Income‑tax Act. Any remittance potentially taxable in India must have appropriate TDS deducted before payment. Rule 37BB mandates reporting of the remittance via Form 15CA and, if applicable, Form 15CB. Both must be submitted electronically before the remitter obtains an American Express Form A‑2 or other regulatory approvals.
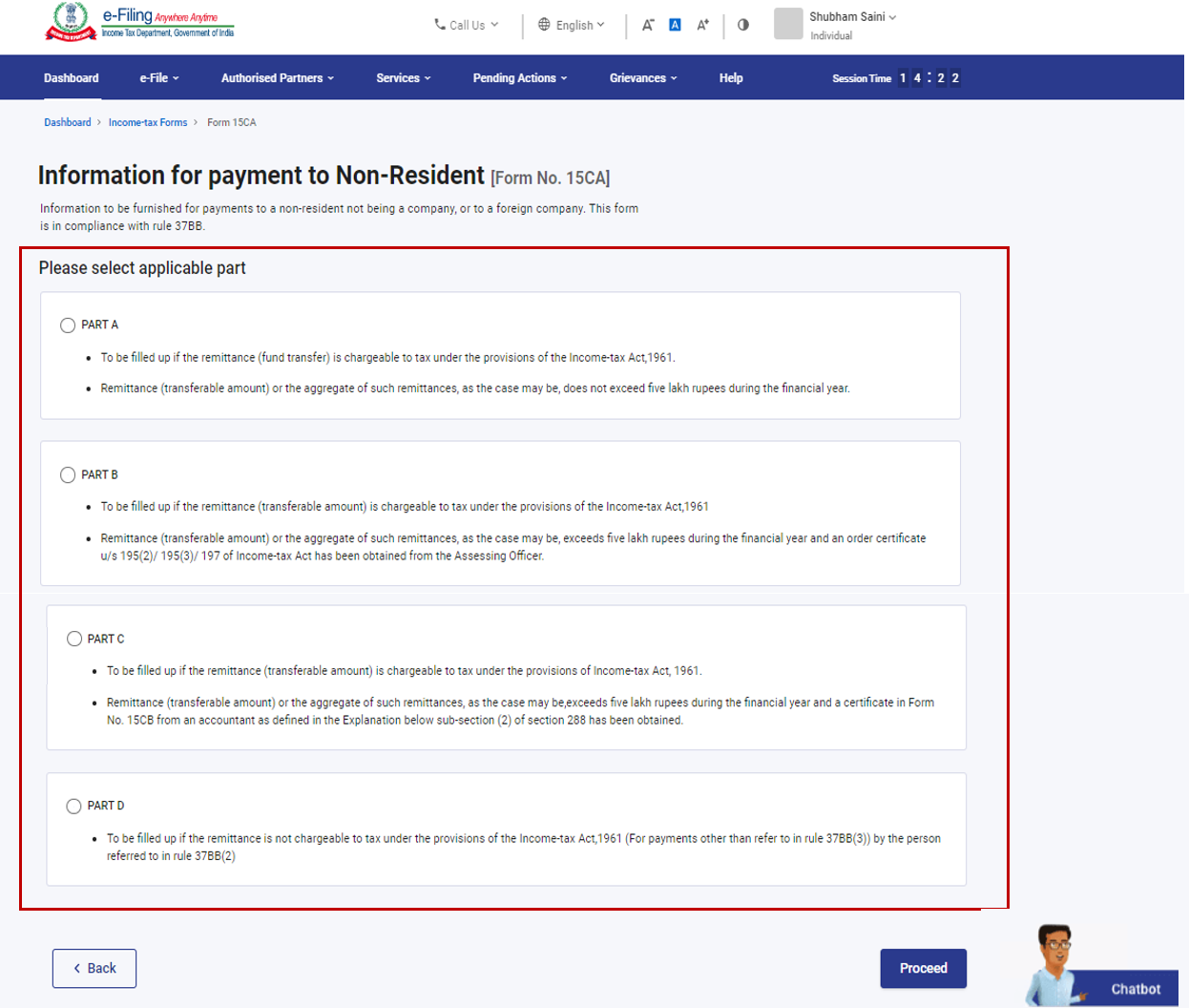
Applicability and Transaction Categories
Form 15CA has four parts Part A through D depending on the nature and amount of remittance:
-
Part A: For specified remittances up to ₹5 lakh cumulatively in a financial year, where either no tax is required to be deducted or taxes will be withheld later.
-
Part B: When remittance is made against payments chargeable to tax but no Certificate of Deduction exists, or remittance is below ₹5 lakh.
-
Part C: Mandatory when Form 15CB is required (i.e., remittances above ₹5 lakh where tax is deductible).
-
Part D: For all other remittances where Part C is not applicable but tax is deductible.
Choosing the correct part is essential, as incorrect usage may result in processing delays or penalties.
Step-by-Step Filing Process for Form 15CA
-
Login to the Income‑tax e‑filing portal at income‑tax.gov.in
-
Navigate to: e‑File → e‑File in offline mode → Form 15CA (Part A/B/C/D)
-
Open the applicable form and input the details offline (date, remitting bank, payment type, amount, country of remittance, whether TDS is applicable, etc.)
-
Attach Form 15CB if you are filing Form 15CA‑Part C. Form 15CB includes certification from a CA about income classification and TDS deduction
-
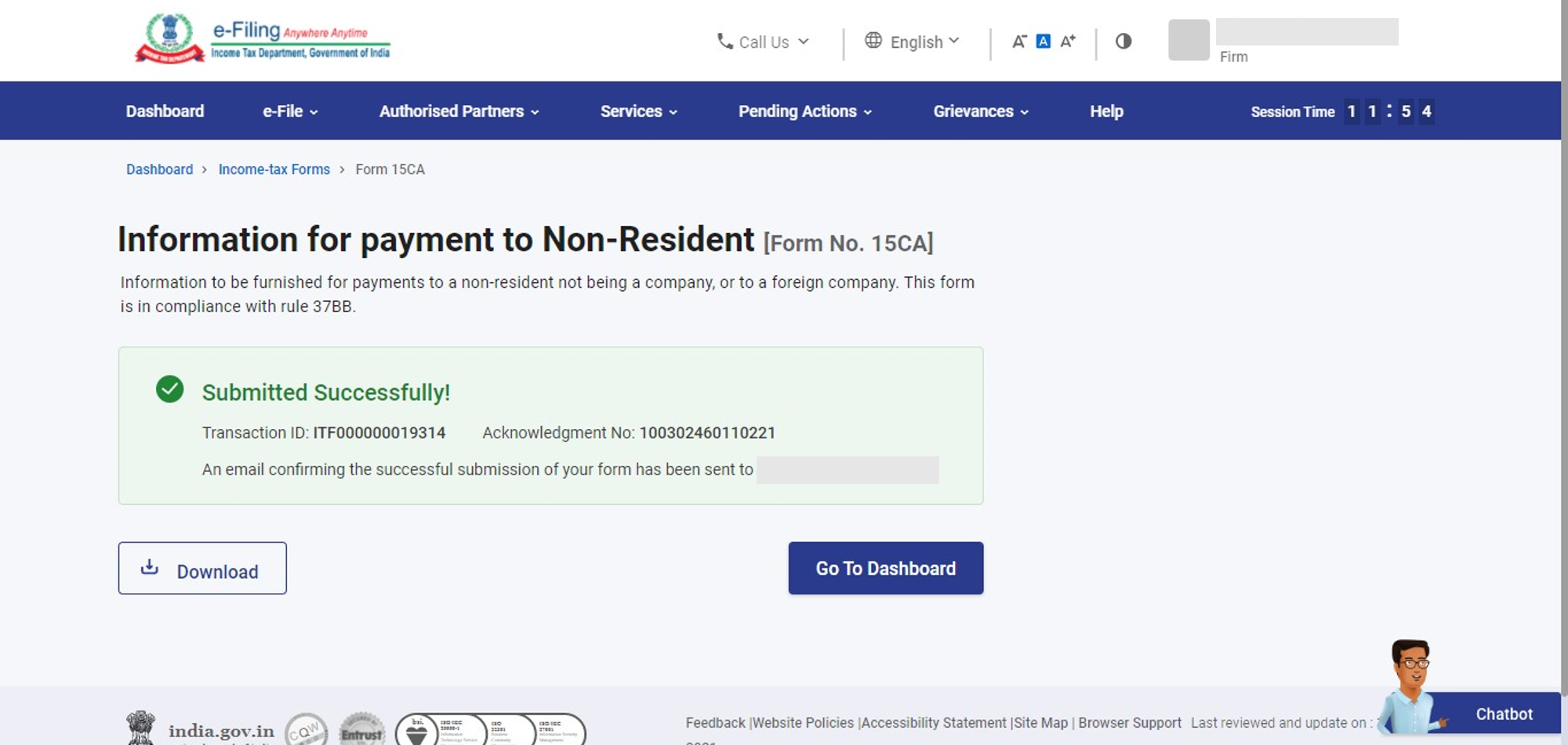
Generate the XML and upload it via e‑File → Upload e‑Forms → Form 15CA
-
Upon uploading, you receive an acknowledgement with a temporary token
-
Provide the token or final XML to the authorized dealer (bank) to process the remittance
When Is Form 15CB Required?
Form 15CB is required for remittances chargeable to tax in India and exceeding ₹5 lakh in aggregate per financial year. A Chartered Accountant must examine:
-
The nature of remittance (royalty, dividend, professional fees, interest)
-
The applicable tax treaties between India and recipient country
-
TDS computation and deduction eligibility
-
Apply reduced treaty rates where applicable
Form 15CB confirms the assessee has fulfilled TDS obligations before remittance.
Documentation Required
A CA completing Form 15CB will need the following:
-
Remittance purpose and nature of payment
-
Recipient’s bank details and residency status
-
Foreign tax certificates or declarations
-
Certificates of TDS deduction (Form 16A, Form 16BB)
-
Agreement or invoice specifying the payment terms
-
Proof of payment execution (wire instructions, foreign bank account)
Always maintain the documentation in physical or digital format for at least six years.
Common Remittance Transactions Covered by Form 15CA
Form 15CA applies to a wide range of transactions, for instance:
-
Payments for overseas merchandise purchases
-
Service payments to foreign consultants, freelancers, or agencies
-
Fee for professional or technical services
-
Interest and dividends payable to overseas investors
-
Royalties, licence fees, franchise charges
-
Purchase or acquisition of off‑shore assets
Different parts of Form 15CA apply depending on transaction value and tax applicability.
Pitfalls to Avoid When Filing Form 15CA
-
Incorrectly selecting Parts A–D
-
Uploading Form 15CA without required Form 15CB
-
Missing TDS or claiming incorrect exemptions
-
Late filing remittance cannot be processed without acknowledgement
-
Failing to reconcile Form 15CB figures with Form 26AS
-
Ignoring treaty benefits and applying incorrect higher TDS rates
-
Not storing proof of filing and acknowledgement
Recommendations and Best Practices
-
File early submit Form 15CA before approaching the bank
-
Seek treaty advice via a CA before remitting
-
Maintain separate ledgers for remittances to track ₹5 lakh thresholds
-
Save XML and acknowledgement token; forward to bank promptly
-
Reconcile TDS deducted with tax credit in Indian returns
-
Store supporting documents securely in case of tax authority query
Record Keeping and Retention
Best practice is to retain digital copies and physical forms for at least six years from the end of the relevant financial year. Make sure each Form 15CA submission is backed up with:
-
Acknowledgement token
-
Form 15CB (if applicable)
-
Supporting invoices and agreements
-
Payment proofs and bank forms
Consequences of Non‑compliance
-
Bank will not process remittance without valid Form 15CA
-
Notice or penalty under Section 271‑I for non‑filing or mistakes
-
Risk of disallowance of expenses or foreign tax credits
-
Potential legal consequences under RBI regulations
Interaction with LRS and RBI Regulations
Form 15CA filing is separate from Liberalised Remittance Scheme (LRS) limits (USD 250,000). You must file Form 15CA regardless of LRS regime. RBI may also ask for declarations independently.
FAQ – Frequently Asked Questions on Form 15CA
-
Do I need both Form 15CA and 15CB?
Form 15CA is mandatory in all cases; Form 15CB is required when remittance exceeds ₹5 lakh or is taxable. -
Can I file Form 15CA online?
Yes, via Income‑tax e‑filing portal and offline jar utility. -
What happens if the Form is filed late?
Your bank will freeze the remittance until valid Form 15CA is submitted, and you may face penalties. -
Is there a fee for filing Form 15CA?
No, it is free to submit through the income‑tax portal. -
Can an NRI file Form 15CA?
No. It applies only to residents making outward remittance. -
Do I need a CA for Form 15CB?
Yes. A practicing Chartered Accountant must certify Form 15CB. -
Can I file Form 15CA‑Part C without Form 15CB?
No. Part C without Form 15CB will be rejected by the system. -
After filing 15CA, how long before remittance can happen?
Usually your bank requires the acknowledgement token; processing time varies per bank. -
Does your bank file 15CA on your behalf?
No. The remitter is responsible, although banks may assist. -
If remittance is below ₹5 lakh, can I file Part A?
Yes, if no tax liability arises and TDS is not withheld at source.
Need Help Filing Form 15CA or 15CB?
Navigating foreign remittance compliance can be tricky but you don’t have to do it alone. At Tradeviser, our team of Chartered Accountants and compliance experts specialize in end-to-end assistance for international transactions, Form 15CA/CB filing, FEMA advisory, and tax planning.
Reach out to Tradeviser today for expert consultation and ensure your remittances are smooth, compliant, and penalty-free.

CA Madhusmita Padal is a Practicing Chartered Accountant with firms based in Odisha and Chennai. She specializes in taxation, company law, and auditing. She is passionate about simplifying complex concepts and making knowledge accessible to all.